OOPs concept
OOPs is stand for (Object Oriented Programming System) OOPs is a methodlogy to design a program using object and class. it simplifies the software development and maintanance by providing some concepts :
- object
- class
- inheritance
- abstraction
- encapsulation
- polymorphism
Advantage of OOPs:
- In this structure of the program is very simple, which reduces the complexity.
- We need to write the code only once in it and we can use it again and again.
- It provides data redundacy.
- In this, we can easily maintain the code, which saves time.
- Data hiding and abstraction are used on OOPs (Object Oriented Programming System) so that in this the security becomes better.
- If debugging is to be done in it then it can be done easily.
Object
- object is an instance of class. All the members of the class can be accessed through object.
- object is having states and behaviours in which states means data and behaviours means functionlity.
- Object means a real word entity such as pen, chair, table etc.
Class
- It is also called userdefined data type.
- It is a collection of data members and members functions.
- Data members are the variable used inside class.
- Members functions are the function used inside class.
- Which can accessed and use by creating object of that class.
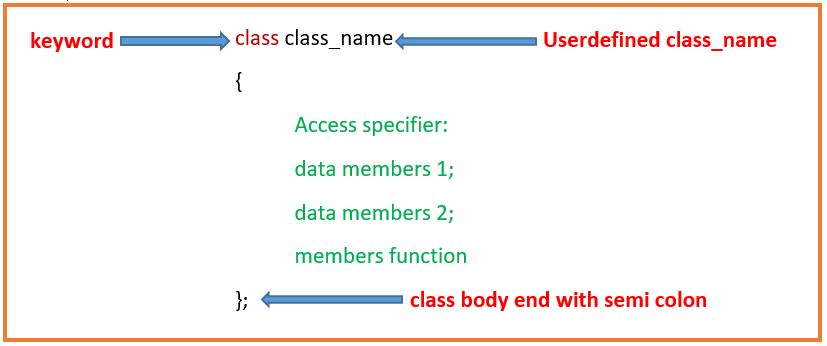
Syntax:
class class_name
{
access specifier
data member
member function
};
- class is a keyword.
- class_name is a user-defined.
- access specifier it is used to accessibility of data member and member function. it may be public, private or protected
- Data member means we can take variables as per user requirment.
- member function means we can take many function as per user requirment.
Example:
#include< iostream.h >
class rect
{
public: //access specifier
int height; // data member
int width;
int area;
void findarea() // memeber function
{
area=height*width;
cout<< "Area of rectangle ="<< area;
}
};
void main()
{
rect rect1; // createing object
rect1.height=20;
rect1.width=30;
rect1.findarea(); calling function through object
}
Output: